Newton's Law of Restitution
Newton's Law of Restitution states that if two particles collide:
e (speed of approach) = (speed of separation)
where e is the coefficient of restitution .
Example
Particle A is travelling at 2m/s. Particle B is travelling in the opposite direction at a speed of 1m/s. After the particles collide, A is brought to rest. If the coefficient of restitution between the particles is ½, what will the speed of B be after the collision?
Let the speed of B after the collision be v (ms-1).
Image
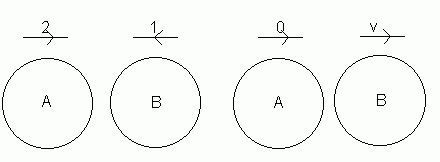
A and B are approaching each other at a speed of 3m/s (2 + 1)
Using Newton's Law of Restitution:
e(speed of approach) = (speed of separation)
½ (3) = v
Therefore the speed of B after the collision is 1.5ms-1
