3D Shapes
A 3D shape is described by its edges, faces, and vertices (vertex is the singular form of vertices).
This video and images below explain the faces, vertices and edges of common three-dimensional shapes.
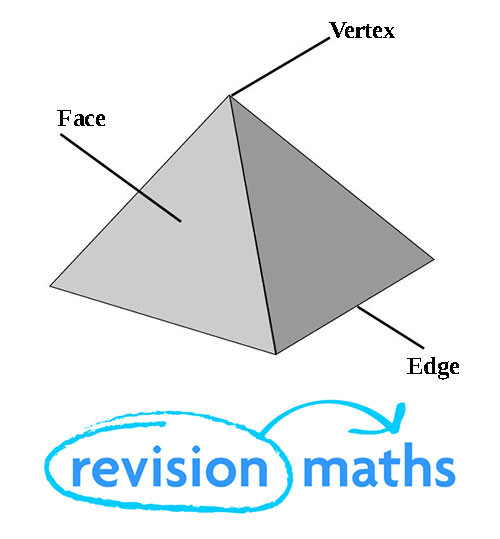
A face is a 2D shape that makes up one surface of a 3D shape, an edge is where two faces meet and a vertex is the point or corner of a geometric shape.
To work out the area of a face of a 3D shape, you use square units such as cm2 as the face of a 3D shape is a 2D shape in its own right (a pyramid’s face will form a triangle, or its base a square). You can learn how to work out area of a shape here.
To work out the volume of the whole 3D shape you used cubic units such as cm3. To learn how to work out the volume of 3D shapes click here.
Properties of 3D Shapes – Prisms
Cube
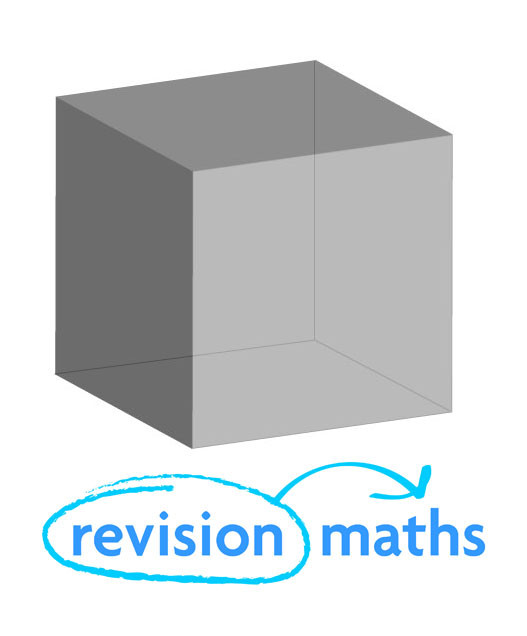
Number of Edges: 12
Number of Faces: 6
Number of Vertices: 8
Cuboid
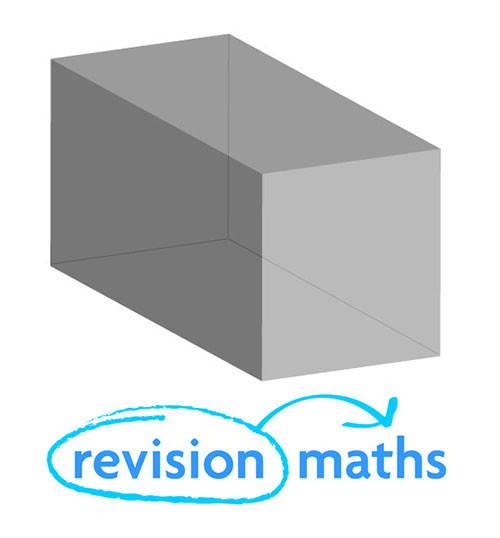
Number of Edges: 12
Number of Faces: 6
Number of Vertices: 8
Cylinder
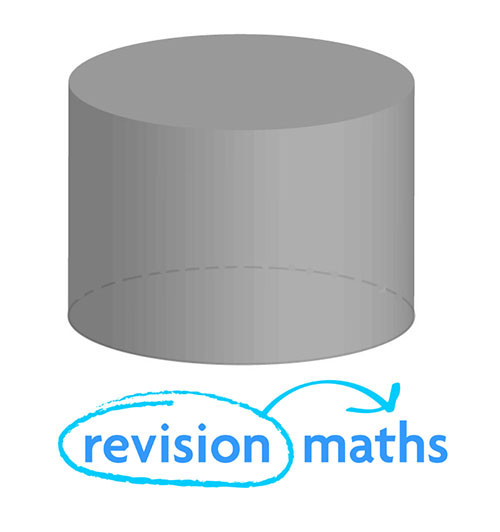
Number of Edges: 2
Number of Faces: 3
Number of Vertices: 0
Triangular Prism
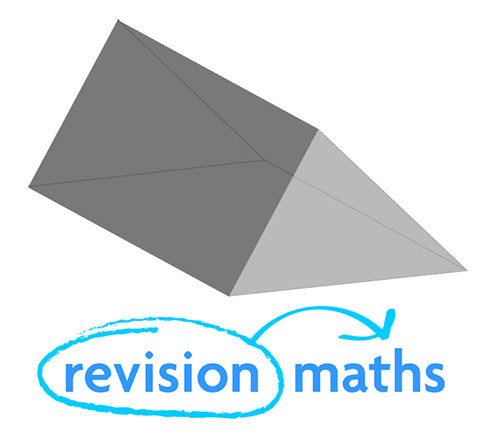
Number of Edges: 9
Number of Faces: 5
Number of Vertices: 6
Octagonal Prism

Number of Edges: 24
Number of Faces: 10
Number of Vertices: 16
Properties of 3D Shapes – Pyramids
Tetrahedron

Number of Edges: 6
Number of Faces: 4
Number of Vertices: 4
Square based Pyramid

Number of Edges: 8
Number of Faces: 5
Number of Vertices: 5
Hexagonal based Pyramid
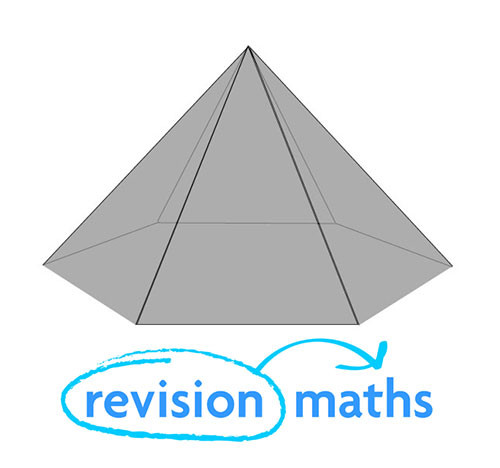
Number of Edges: 12
Number of Faces: 7
Number of Vertices: 7
Properties of 3D Shapes – Curved Faces
Cone
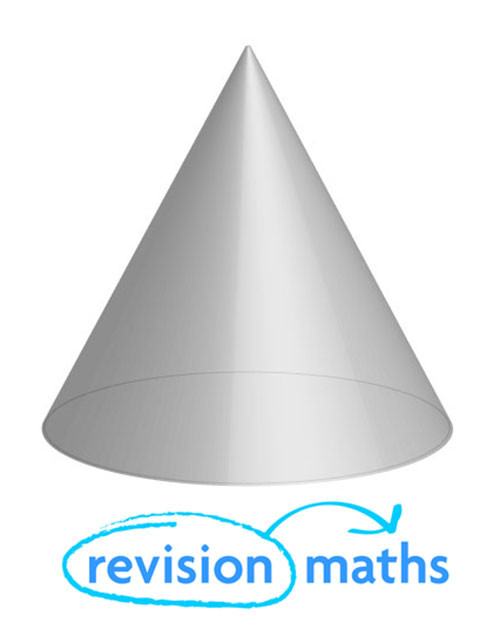
Number of Edges: 1
Number of Faces: 2
Number of Vertices: 1
Frustum

Number of Edges: 2
Number of Faces: 3
Number of Vertices: 0
Sphere
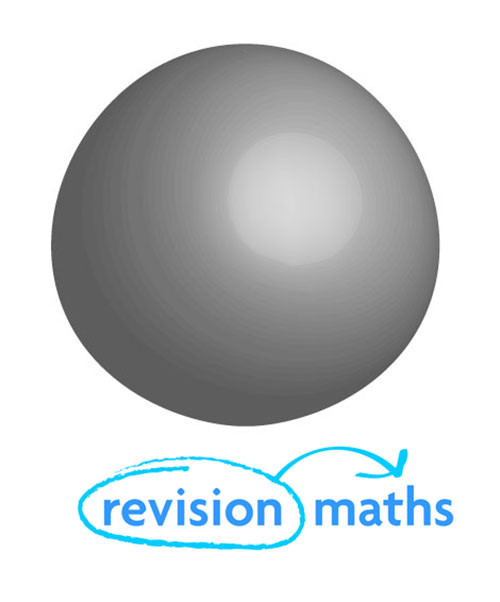
Number of Edges: 0
Number of Faces: 1
Number of Vertices: 0
